Call us at
Email us at
Menu
How it all works
How Does a Solar Energy System Work?
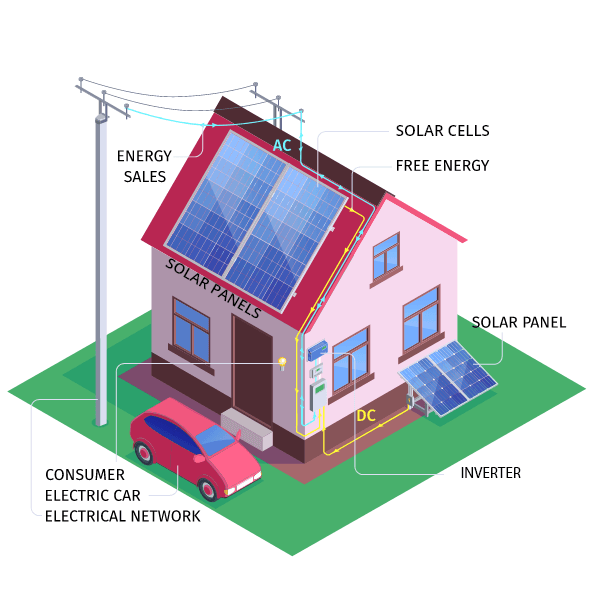
- Solar panels collect clean, renewable energy from the sun, and turn it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- An inverter changes power from your solar panels into alternating current (AC), the type of electricity you need to power your home.
- To store excess energy for later use, you can install a battery backup system. Use saved electricity at night or return it to the grid during peak hours for a greater utility credit
What Are Solar Panels?
- Solar panels are made up of an array of solar cells held together by glass, a laminate material (EVA), and an aluminum frame.
- Solar cells are able to capture energy from the sun to generate electricity, much like a leaf catching sunlight to generate food for a plant. One solar cell doesn’t produce much on its own—maybe enough to power a calculator. Therefore, an array of solar cells is connected to create one large solar panel. Panels are linked together to provide enough energy to power your home.
- Most solar cells are made from silicon, which is also used in computers and smartphones. Silicon is a semiconductor that has photovoltaic (PV) properties, meaning it generates voltage and electric current when exposed to light.
- To make solar cells, silicon is mixed with small amounts of phosphorus or boron to create an abundance of electrons (p-type) or lack of electrons (n-type). The different types of silicon are made into plates and sandwiched together. Metallic conductors are attached to each side, and everything is held in place by a laminate material.
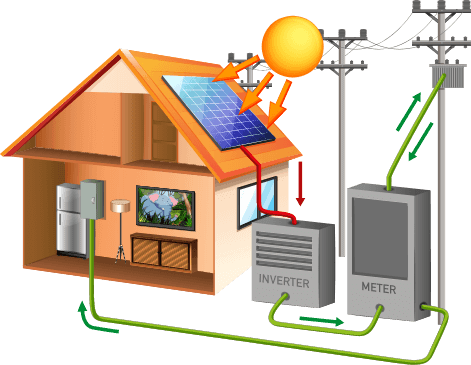
How Do Solar Panels Work?
When sunlight hits the PV material in the form of photons, electrons are knocked out of place. Due to the layering of p-type and n-type PV material, loose electrons begin to flow in one direction. This electricity travels on metallic conductors in the form of direct current to an inverter.
The inverter changes the electricity from direct current to alternating current that can be used to power your home.
What Are the Different Types of Solar Panels?
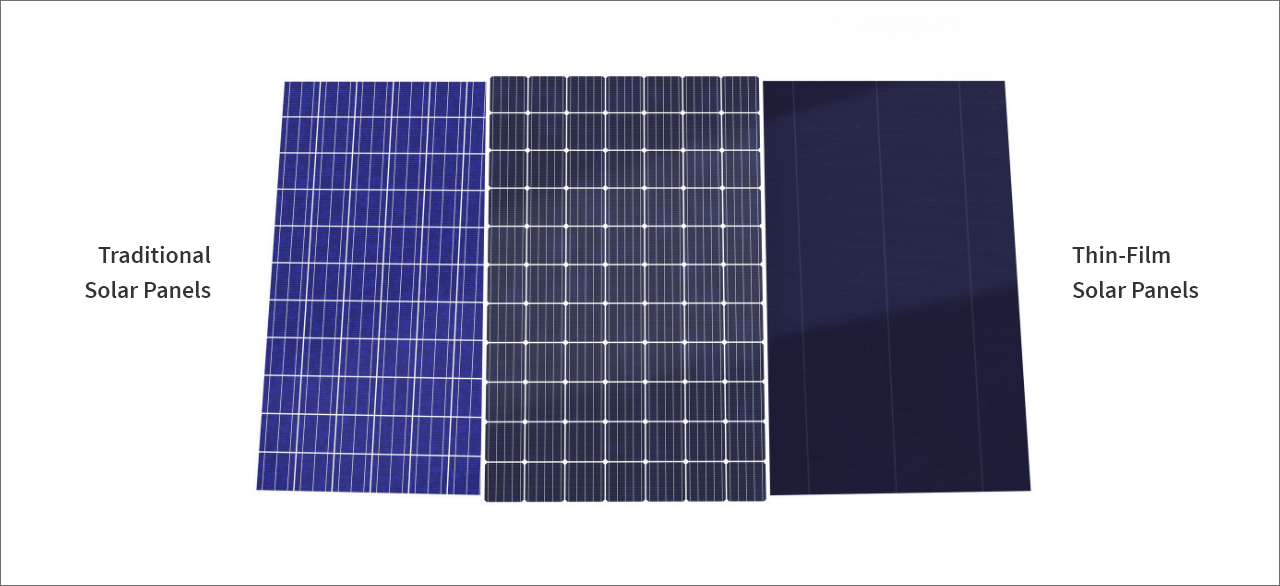
Traditional Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are made up of single crystal silicon that is melted into an ingot and thinly sliced. This creates a more refined, more efficient, but also more expensive product. Monocrystalline solar panels are a great choice for homes where roof space is limited since they’re so efficient. They usually appear black in color.
Polycrystalline panels are made up of lots of silicon crystals melted together. They’re not quite as efficient as monocrystalline panels, but they’re also more affordable. If you have plenty of space, this may be a good choice for your home. Polycrystalline solar panels will appear dark blue.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin layers of photovoltaic (PV) material are placed on a conductive sheet and covered with a protective material like glass or plastic to make thin-film solar panels. They’re light and flexible but are currently much less efficient than either of the traditional options. Because they’re easier to manufacture, they are also more affordable than traditional panels.
How Do I Save Money With Solar?
Collect & Convert Energy
Solar panels collect energy from the sun and convert it into electricity for your home. Whenever the sun’s out, you’ll be generating your own electricity—free of charge.
Net Energy Metering (NEM)
Your system may generate more electricity than you need for your home at one time. When this happens, the excess power is sent to the utility grid, and you receive energy credits.
Ready to Go Solar?
Getting your own solar energy system has never been easier. Schedule your free consultation today to learn if Solar 360 is right for you!